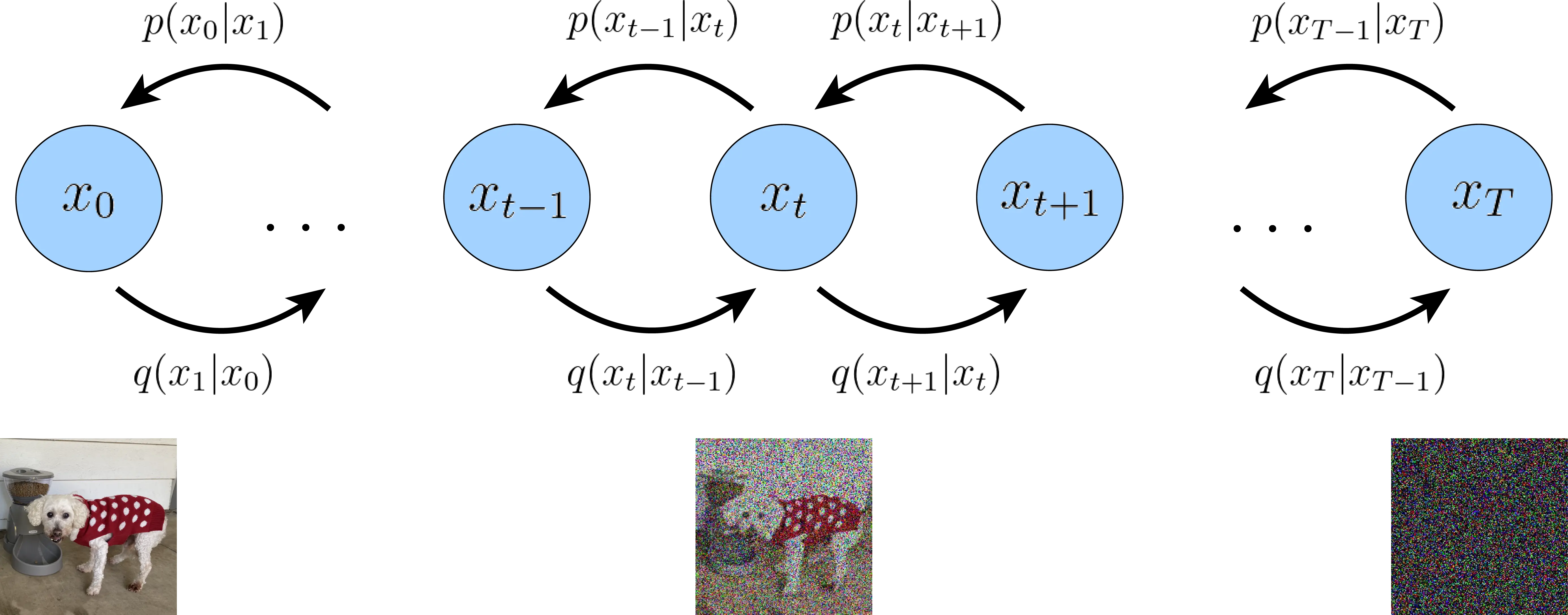
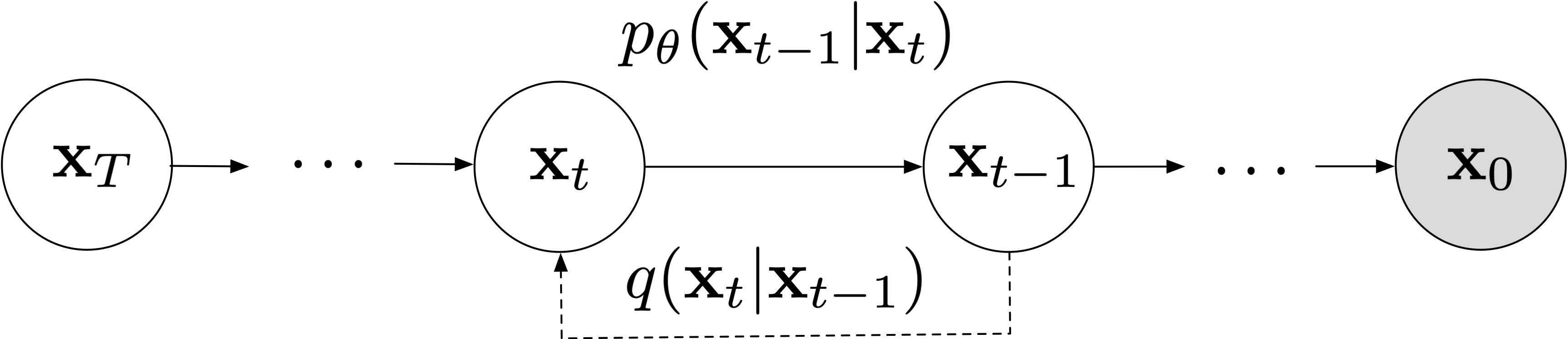Diffusion & Generative Modeling
Diffusion processes, flows, GAN/CTGAN, CFG tricks, and other approaches to high-dimensional generation.
-
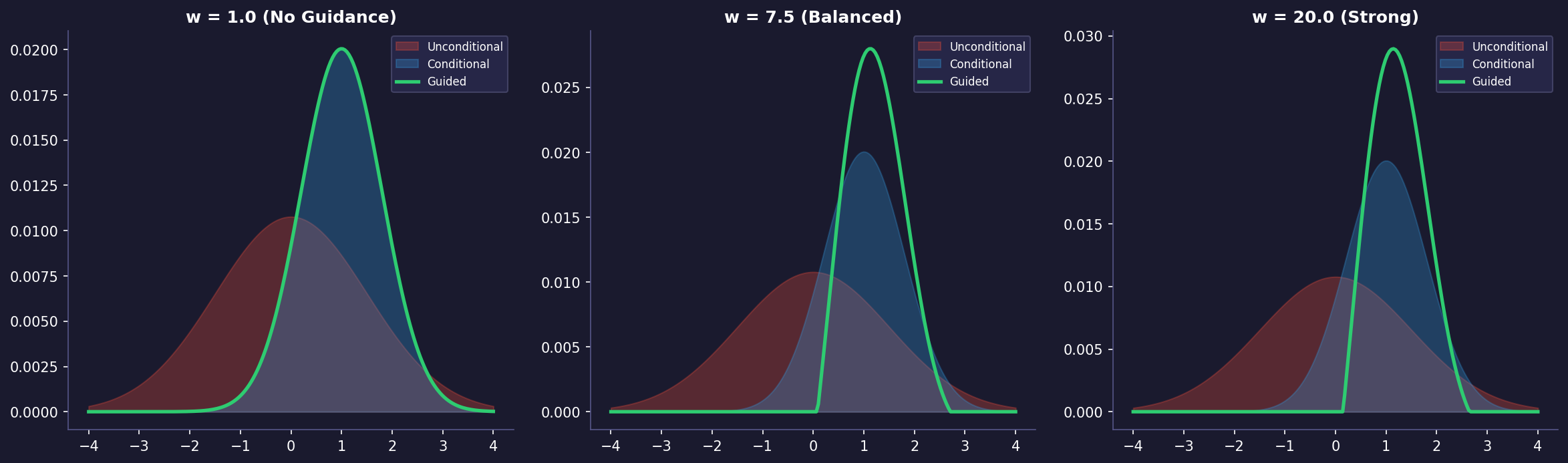
· Classifier free diffusion guidance
One of the key techniques in diffusion models that has significantly improved their performance is classifier-free guidance. In this post, we'll explore what classifier-free guidance is, how it works, and implement it from scratch in PyTorch.
-
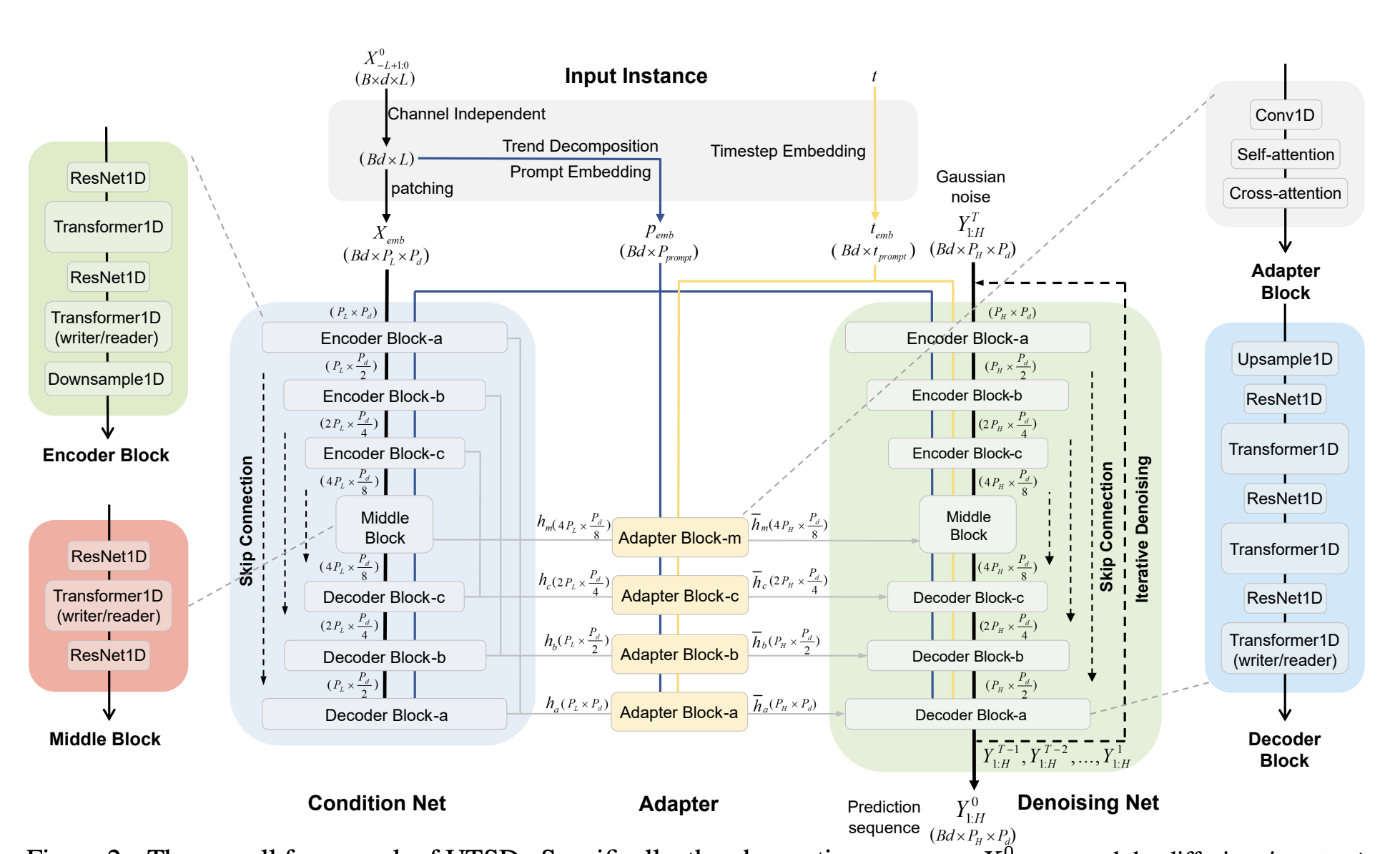
· Diffusion models for time series
On this post I will explore the main findings from the paper UTSD: Unified Time Series Diffusion Model and an explanation of the content. For more details here is the link to the paper Link to paper
-
· Flow Matching, a short overview
In summary, flow matching is a generative modeling technique that provides an elegant way to transform data distributions.
-
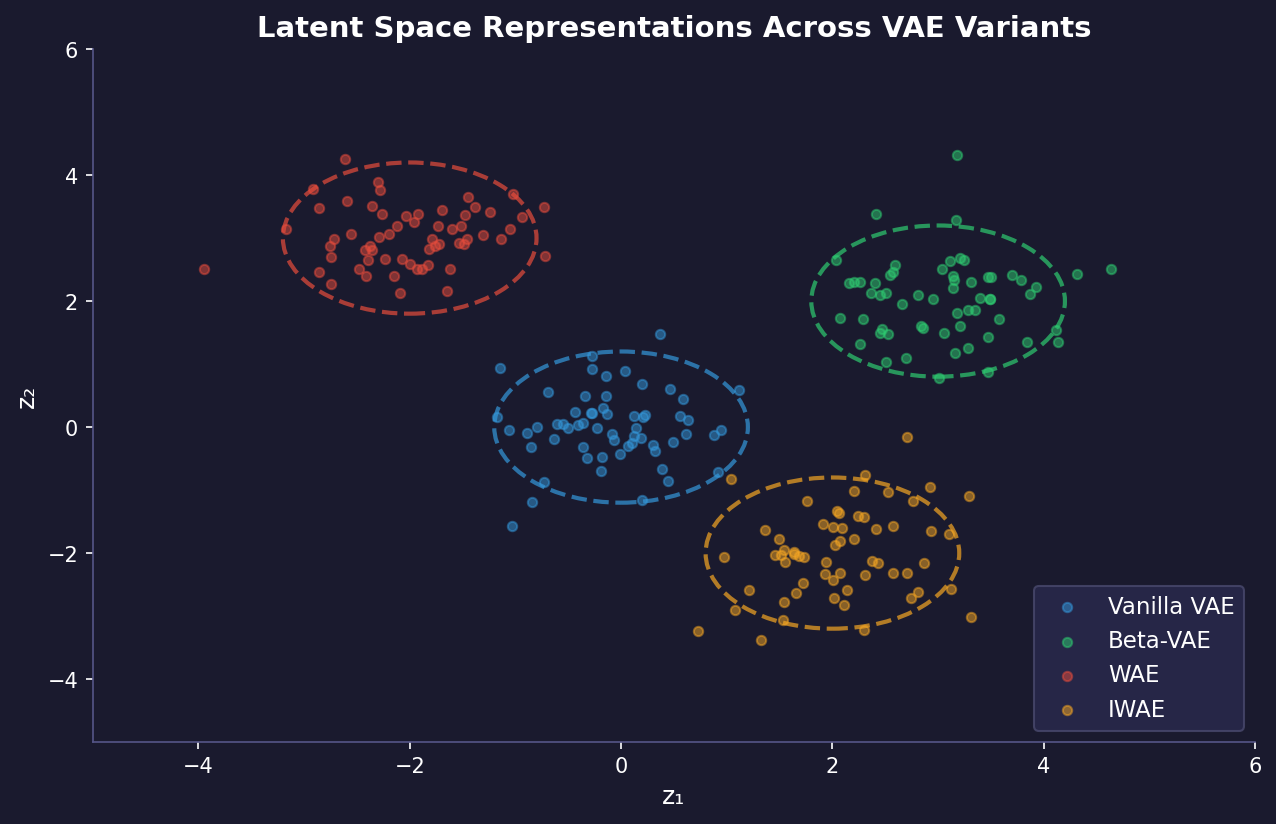
· A comprehensive list of different types of VAEs
VAE (Vanilla VAE): The original VAE architecture consists of an encoder that maps input data to a latent space, and a decoder that reconstructs the input from the latent representation. It uses a variational inference approach to learn the latent space distribution.
-
· DDIM vs DDPM
Diffusion models have emerged as a powerful class of deep generative models, particularly excelling in image synthesis tasks. This article delves into a comprehensive comparison of two significant variants: Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) and Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIM).
-
· Diffusion models or Autoencoders?
Recent advancements in generative AI have brought diffusion models to the forefront, particularly for their impressive performance in image generation. While these models are often seen as distinct from traditional approaches, there's a compelling argument for viewing diffusion models as a form of hierarchical autoencoder.
-
· Conditional Tabular GAN - CTGAN
One of the most interesting ideas on the last decades in machine learning is the GAN architecture for generatine model. While GANs have shown remarkable success in generating high-quality images and other continuous data types, tabular data poses unique challenges. Tabular data often contains a mix of discrete and continuous variables, with complex dependencies between them. Traditional GAN architectures struggle to capture these intricacies, leading to poor performance when applied directly to tabular data. CTGAN addresses these challenges by introducing a specialized framework for generating realistic synthetic tabular data.