Flow Matching, a short overview
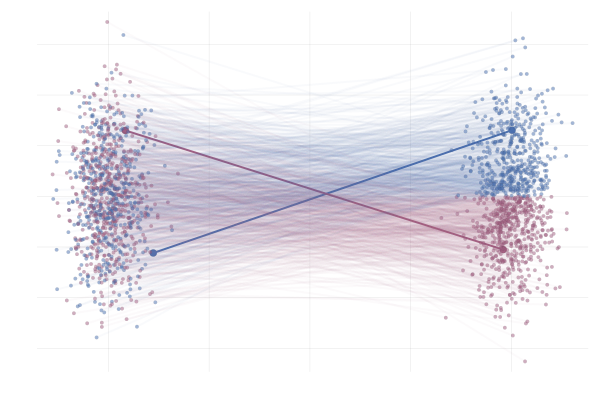
In summary, flow matching is a generative modeling technique that provides an elegant way to transform data distributions.
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
class FlowMatchingModel:
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim):
"""
Initialize Flow Matching Model
Args:
input_dim (int): Dimension of input data
hidden_dim (int): Dimension of hidden layers
"""
self.base_distribution = None # Initial data distribution
self.target_distribution = None # Target data distribution
# Neural network to learn the flow
self.flow_network = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_dim + 1, hidden_dim), # +1 for time conditioning
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, input_dim)
)
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.flow_network.parameters())
def sample_base_distribution(self, num_samples):
"""
Sample from the base (initial) distribution
Args:
num_samples (int): Number of samples to generate
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Samples from base distribution
"""
# Example: Gaussian distribution
return torch.randn(num_samples, self.input_dim)
def probability_flow_ode(self, x, t):
"""
Compute the probability flow ODE
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): Current data point
t (torch.Tensor): Time variable
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Flow direction
"""
# Combine input and time as network input
network_input = torch.cat([x, t], dim=1)
return self.flow_network(network_input)
def conditional_vector_field(self, x0, x1, t):
"""
Compute the conditional vector field
Args:
x0 (torch.Tensor): Initial data point
x1 (torch.Tensor): Target data point
t (torch.Tensor): Time variable
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Conditional vector field
"""
# Interpolate between source and target
x_t = x0 * (1 - t) + x1 * t
vector_field = x1 - x0
return vector_field
def loss_function(self, x0, x1):
"""
Compute the flow matching loss
Args:
x0 (torch.Tensor): Initial data points
x1 (torch.Tensor): Target data points
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Training loss
"""
batch_size = x0.shape[0]
t = torch.rand(batch_size, 1) # Random time sampling
# Compute vector field
true_vector_field = self.conditional_vector_field(x0, x1, t)
predicted_vector_field = self.probability_flow_ode(x0, t)
# Compute MSE loss between true and predicted vector fields
loss = torch.mean((predicted_vector_field - true_vector_field) ** 2)
return loss
def train(self, dataloader, epochs):
"""
Train the Flow Matching Model
Args:
dataloader (torch.utils.data.DataLoader): Training data
epochs (int): Number of training epochs
"""
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch_x0, batch_x1 in dataloader:
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = self.loss_function(batch_x0, batch_x1)
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss: {loss.item()}")
def generate_samples(self, num_samples):
"""
Generate new samples using the learned flow
Args:
num_samples (int): Number of samples to generate
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Generated samples
"""
# Start from base distribution and follow the learned flow
x0 = self.sample_base_distribution(num_samples)
# Perform sampling through ODE solving
x_generated = x0 # Starting point
time_steps = torch.linspace(0, 1, 100)
for t in time_steps[1:]:
vector_field = self.probability_flow_ode(x_generated, t)
x_generated += vector_field * (time_steps[1] - time_steps[0])
return x_generated
def main():
# Hyperparameters
input_dim = 10
hidden_dim = 64
num_epochs = 100
flow_matching = FlowMatchingModel(input_dim, hidden_dim)
flow_matching.train(dataloader, num_epochs)
generated_samples = flow_matching.generate_samples(1000)