Math, Physics & Foundations
Hopfield networks, Kalman filters, Kolmogorov ideas, probability, information theory, and philosophical musings.
-
· From Entropy to Epiplexity
In this paper https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03220, Finzi et al. argue that classical information theory (Shannon entropy and Kolmogorov complexity) is insufficient for understanding modern AI because it assumes an observer with unlimited computational power. Under classical theory, deterministic transformations cannot create new information, yet empirically, processes like self-play (AlphaZero) and synthetic data generation clearly improve model capabilities.
-
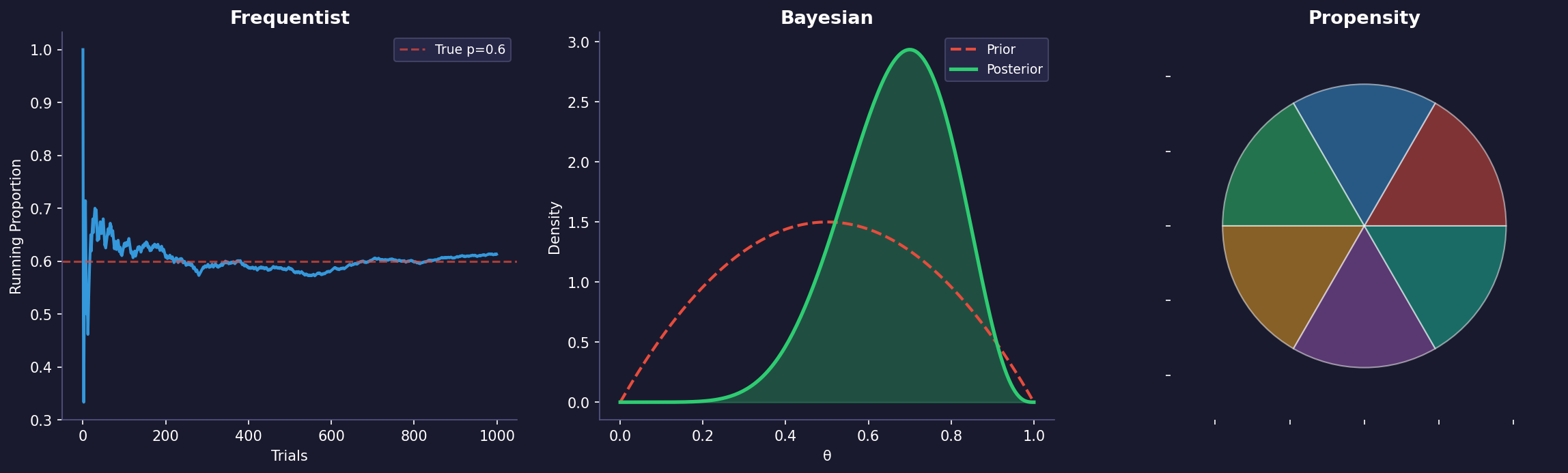
· Probability Paradigms
When we think about probability, there are three main philosophical approaches: frequentist, Bayesian, and propensity. Each offers a different lens for understanding uncertainty and probability.
-
· The Platonic Representation Hypothesis: Are AI Models Converging on Universal Representations?
This blog post is based on The Platonic Representation Hypothesis by Huh et al. (2024), MIT. AI models are becoming increasingly similar in how they represent the world, regardless of how they're trained or what kind of data they process. This fascinating trend suggests we may be approaching a universal way of representing reality.
-
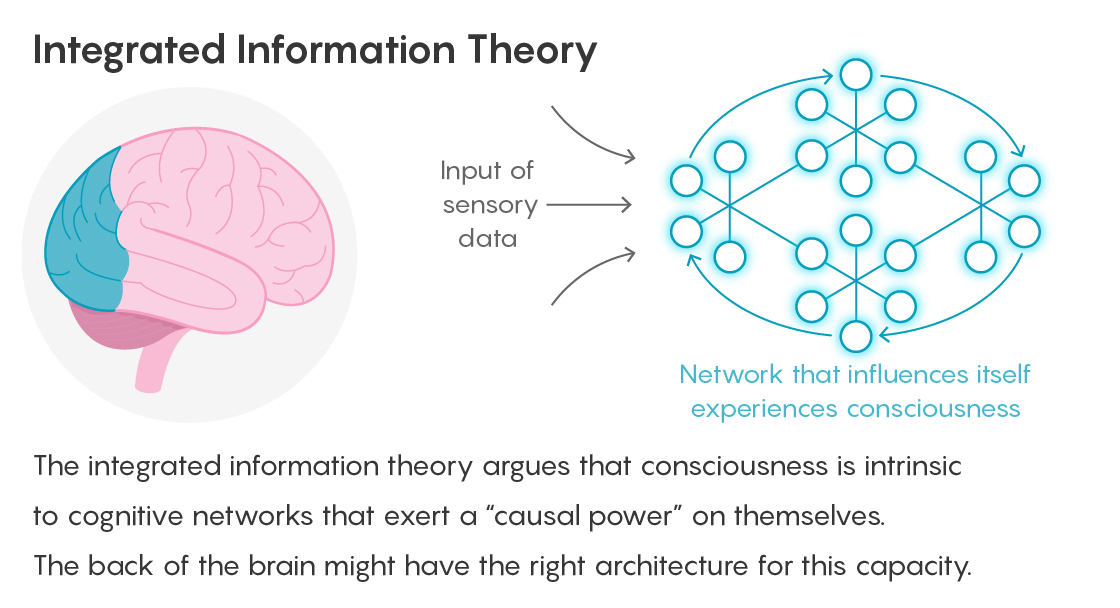
· Integrated Information Theory (IIT)
One of the most interesting question to be made is about the nature of consciousness. During a long time the question of consciousness was considered as a philosophical question but during the last decades this question has been approached by the science with the emergence of the Integrated Information Theory (IIT) by Giulio Tononi. This paradigm, proposes a radical reconceptualization of consciousness, framing it as an intrinsic property of physical systems, quantifiable through information integration.
-
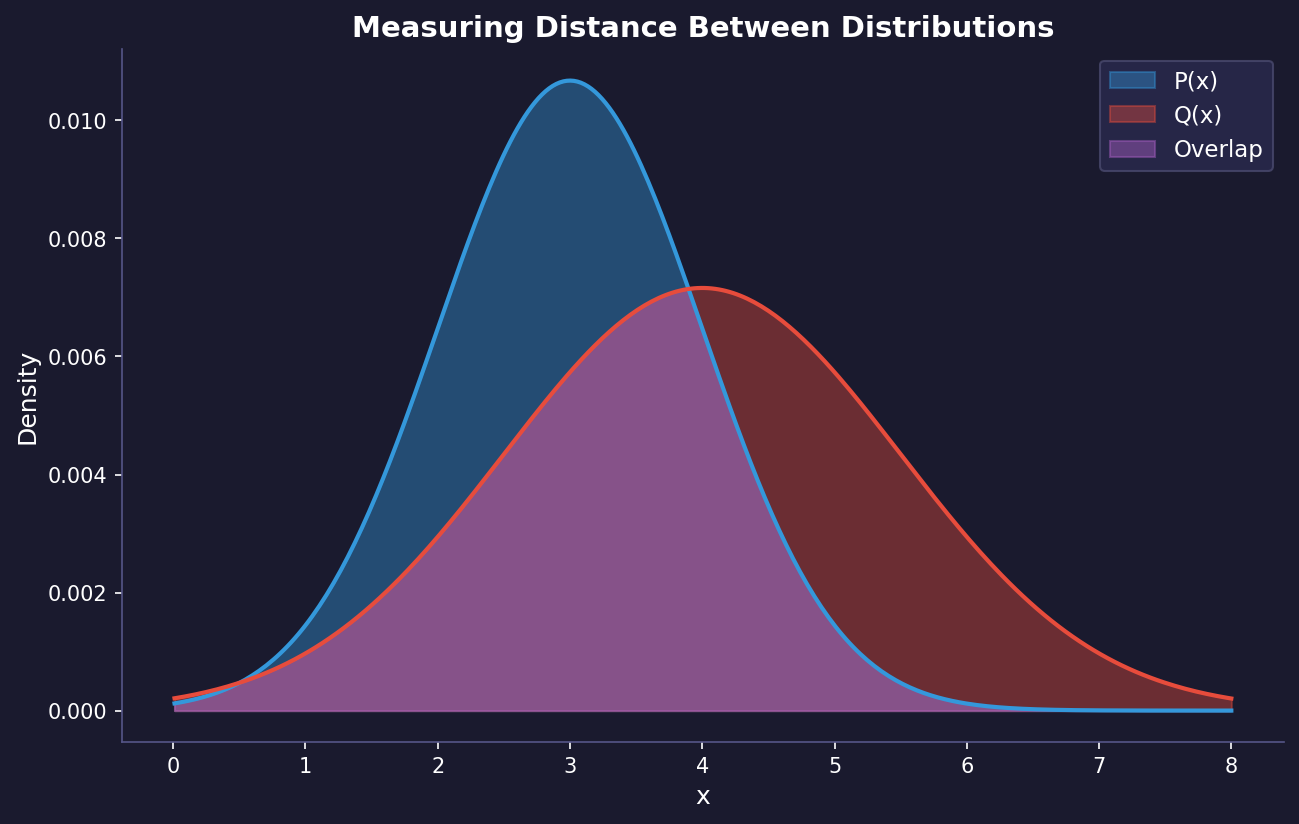
· Some common divergences
Hey. usually on machine learning we have to consider distances between different probability distributions. This is in fact a hard problem and there is a misconception that the most common way to do this is using the kl divergence. I believe that this is not true.
-
· Kolmogorov Complexity
Think of Kolmogorov Complexity as a way to measure the complexity of a string (a sequence of characters) by looking at the length of the shortest possible program that can produce that string. Imagine you have a super-efficient computer program that generates text. Kolmogorov Complexity is about finding the tiniest program that can spit out the exact text you have.
-
· Some tests with the Mandelbrot set and parallelization
Hello. It has been a while since I lasted programed with OpenMP and C. For refreshing my mind and keeping the concepts clear I was doing some tests with the Mandelbrot Set with OpenMP and with a single thread. Here is the code for both cases:
-
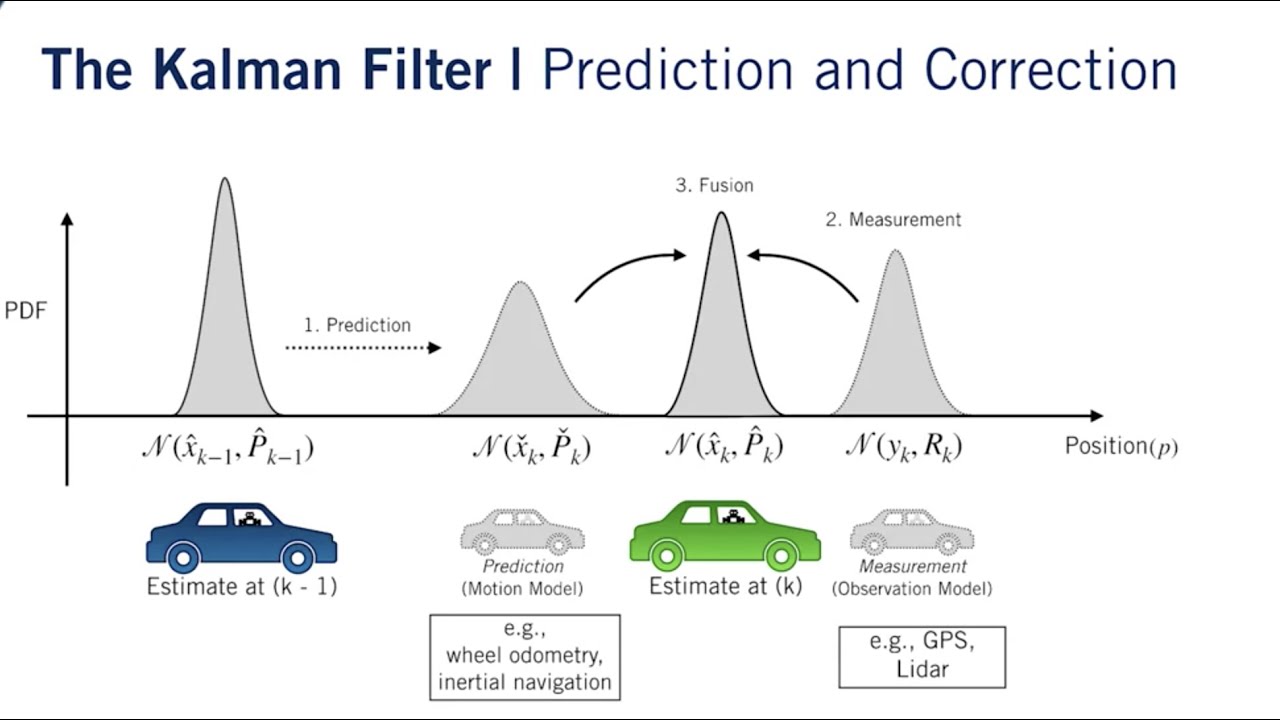
· Implementing the Kalman Filter in Python
Hello. I'm trying to experiment with some recent articles that tries to connect transformers and kalman filter. I remember that I saw in my undergrad this concept on the control lecture but to be honest I didn't quite understand the concept at the time. To help my understanding i tried to implement using only some basic python libraries the Kalman Filter in python.
-
· Implementing from scratch a Hopfield Network
A while ago I posted about Hopfield Networks. I wanted to further explore this theme by trying to implement this type of idea from scratch in python.
-
· Understanding Cover's Universal Portfolio
I always wanted to understandt the concept of a universal portfolio from Cover's. This topic always fascinated me since I first heard about it on my information theory lectures and you know what they say... The best way to learn is to practice. So here's my attempt ...
-
· Hopfield Networks for dummies
Hopfield Networks, a type of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), are renowned for their unique ability to store and retrieve patterns through associative memory. This means they can recall a complete memory from just a partial input. Inspired by the Ising model in physics, which explains magnetic behaviors in certain materials, Hopfield Networks use a system of interconnected neurons, each able to be in one of two states, akin to magnetic dipoles. These neurons are fully connected, each influencing the other based on the strength of their connections. The network dynamically evolves to a stable state where the system's energy is minimized, representing a memory. The overall network state thus can represent binary information, like an image or a pattern, making Hopfield Networks particularly effective in pattern recognition and completion tasks.