Implementing the Kalman Filter in Python
Hello. I’m trying to experiment with some recent articles that tries to connect transformers and kalman filter. I remember that I saw in my undergrad this concept on the control lecture but to be honest I didn’t quite understand the concept at the time. To help my understanding i tried to implement using only some basic python libraries the Kalman Filter in python.
Before the notebook with the implementation here is a quick summary of what is this filter provided by GPT ( =P ):
A Kalman filter is a powerful algorithm used for making estimates or predictions in systems that are subject to various uncertainties. It’s widely used in fields like robotics, aerospace, finance, and even weather forecasting. Here’s a simplified explanation suitable for a blog post:
-
Understanding the Kalman Filter: A Simple Guide Imagine you’re trying to predict the position of a moving car using a GPS system. The GPS provides you with location data, but this data isn’t perfect—it has some level of inaccuracy or ‘noise’. How do you make the best possible estimate of the car’s true position?
-
Enter the Kalman filter. Developed by Rudolf E. Kalman in the 1960s, this algorithm is a set of mathematical equations that provides an efficient computational (recursive) solution to the problem of estimating the state of a process—in our case, the position and speed of the car.
-
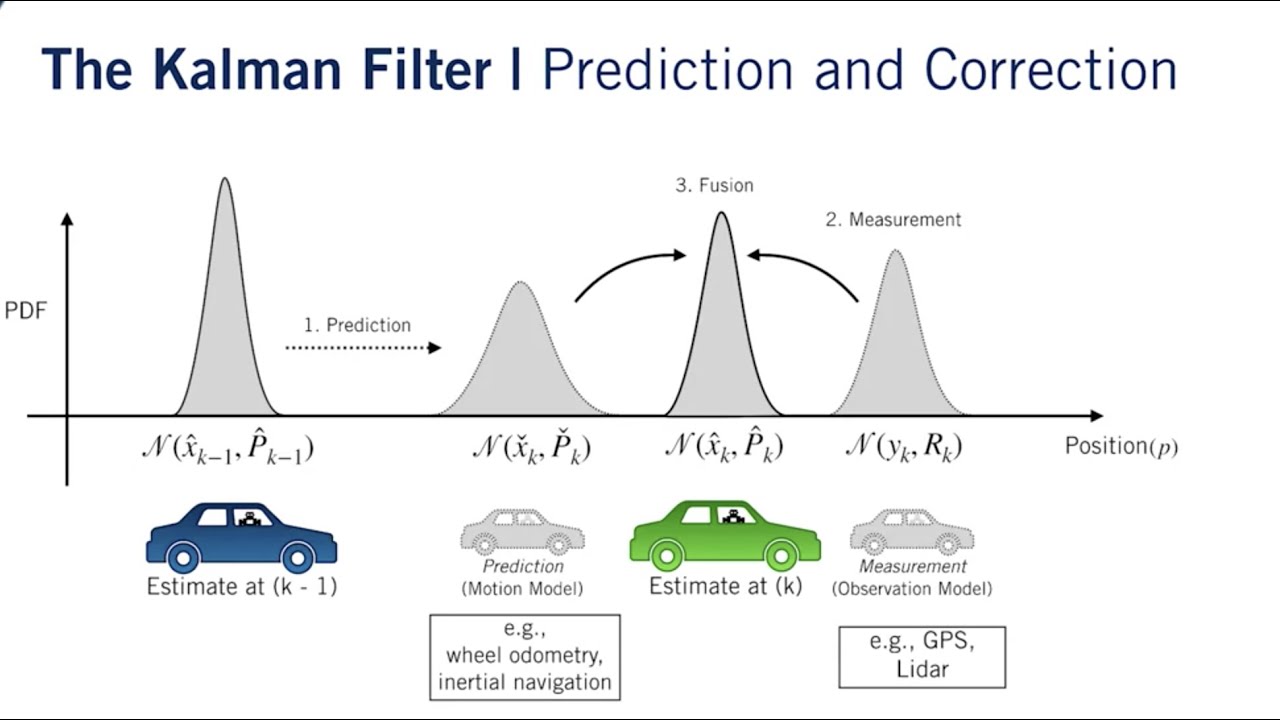
How Does It Work? The Kalman filter works in two fundamental steps: Prediction and Update.
-
Prediction: This step involves predicting the current state of the process (like the position and velocity of the car) based on the previous state. It’s like saying, “Given where the car was and how fast it was moving, here’s where I think it is now.”
-
Update: In this step, the Kalman filter takes new measurements (e.g., from the GPS) and refines the prediction. It essentially asks, “Now that I have new data, how should I adjust my prediction to be more accurate?”
The beauty of the Kalman filter lies in its ability to deal with uncertainty. It’s designed to weigh both the predicted state and the new measurements, considering the uncertainties in both. If the measurements are very accurate, it gives them more weight. If the predictions are believed to be more reliable, it leans more on them.
- Real-World Applications While the GPS example is straightforward, the Kalman filter is used in much more complex situations. It’s vital in the operation of satellites and spacecraft, where precise navigation is crucial. In the financial world, it helps in predicting market trends and in robotics, it’s used for navigation and tracking movements.
Finally here is the notebook : Colab