Implementing the Transformer in Python
Hello everyone. Today the I will present a sketch of a transformer implementations. The focus here will be only on the forward pass of the architecture and not on learning the weights.
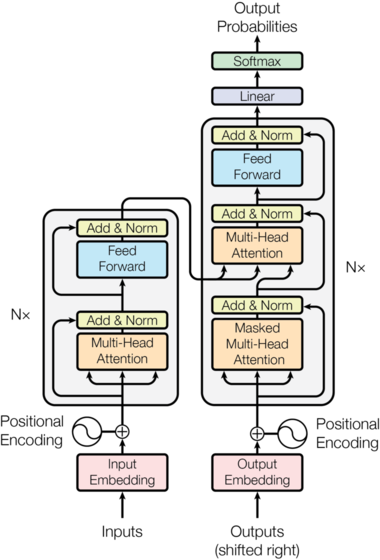
To elaborate further on the technical details of implementing a Transformer model, we can dive into the key components and steps involved in the forward pass of the architecture. The Transformer model, introduced in the paper “Attention is All You Need” by Vaswani et al., is a deep learning model that has revolutionized the field of natural language processing (NLP) due to its effectiveness in handling sequential data without relying on recurrent layers.
Key Components of the Transformer:
-
Input Embedding: The input sequence is converted into a high-dimensional embedding that represents each token in a continuous vector space. Positional encodings are added to these embeddings to provide the model with information about the order of tokens.
-
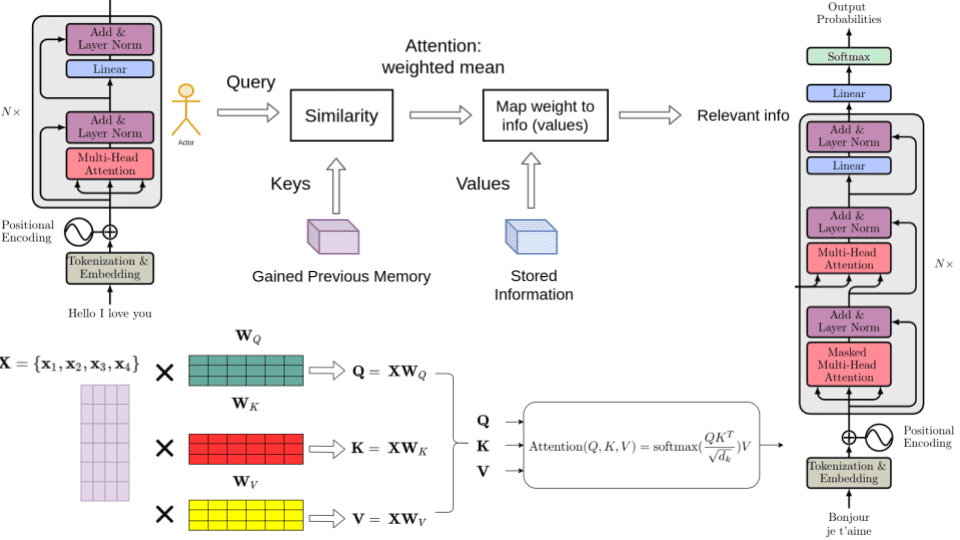
Multi-Head Attention: This mechanism allows the model to focus on different parts of the input sequence simultaneously. It performs scaled dot-product attention multiple times in parallel, and the outputs are concatenated and linearly transformed.
-
Position-wise Feed-Forward Networks: Each position in the encoder and decoder layers passes through a feed-forward neural network, which is applied independently to each position.
-
Normalization and Residual Connections: Each sub-layer (attention and feed-forward networks) in the encoder and decoder is followed by layer normalization and is wrapped with a residual connection. This helps in stabilizing the training of deep networks.
-
Encoder and Decoder: The Transformer model consists of an encoder stack and a decoder stack. The encoder processes the input sequence, and the decoder generates the output sequence, one token at a time. The decoder also uses masked attention to prevent future tokens from being used in the prediction of the current token.
Implementing the Forward Pass:
The forward pass of the Transformer involves processing the input sequence through the encoder layers, followed by the decoder layers to generate the output sequence. Here’s a high-level overview:
-
Prepare Input Embeddings: Convert the input tokens into embeddings and add positional encodings.
-
Encoder: For each encoder layer, perform multi-head attention on the input embeddings and apply the position-wise feed-forward network. Use normalization and residual connections around each of these sub-layers.
-
Decoder: For each decoder layer, perform masked multi-head attention on the decoder input embeddings. Then, perform multi-head attention using the encoder output as key and value, and the output of the previous attention layer as the query. Apply the position-wise feed-forward network, followed by normalization and residual connections.
-
Output Linear Layer and Softmax: The final decoder output is passed through a linear layer followed by a softmax function to predict the probability distribution of each token in the output vocabulary.
Finally here is the notebook with the implementation: Colab